Unraveling Identity: Ethnicity Vs Nationality Explained
Have you ever stopped to think about what truly shapes who we are, or perhaps how we fit into the bigger picture of the world? It's a pretty interesting question, that, and often, folks use terms like "ethnicity" and "nationality" almost interchangeably. But here's the thing: they actually point to quite different aspects of a person's identity. Understanding these distinctions isn't just about getting definitions right; it's about appreciating the rich variety of human experience and the different ways we connect with others and with places.
Knowing the difference between "ethnicity" and "nationality" can be really helpful when learning about different cultures, you know? It’s like knowing the ingredients that make up a recipe for a country. What makes one group unique from another, or what makes someone belong to a particular country? These concepts, while often linked, hold distinct meanings that shape our understanding of identity, culture, and even our place in the wider world, so it's worth exploring.
This discussion isn't just for academics or those studying social sciences; it’s for anyone curious about themselves and the people around them. Really, it helps us see how diverse human societies are, and how different groups celebrate their unique traditions, foods, or languages. So, let’s explore these fascinating distinctions between ethnicity and nationality, and perhaps, you'll gain a clearer picture of how these ideas influence history and society, as a matter of fact.
Table of Contents
- What's the Big Deal? Why These Terms Matter
- Ethnicity: A Shared Cultural Tapestry
- Nationality: Your Legal Tie to a Country
- The Intersections and Differences Between the Two
- Why Understanding These Concepts Is Important
- Frequently Asked Questions
What's the Big Deal? Why These Terms Matter
Understanding the difference between ethnicity and nationality can be really helpful, as I was saying, especially when we talk about identity. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they actually mean different things. One describes where your cultural roots lie, while the other talks about your legal connection to a country. It's pretty important to get this straight to avoid misunderstandings and to appreciate the rich variety of human experiences around the globe.
For example, knowing these distinctions helps us see that within a single country, numerous ethnicities might coexist, each celebrating its unique traditions, foods, or languages. This means a country isn't just one big, uniform group, but rather a collection of many different cultural stories. It’s like knowing the ingredients that make up a recipe for a country, in a way, allowing us to appreciate each distinct flavor.
The concepts of ethnicity and nationality have influenced history and society in many ways, too. They've shaped how people identify themselves, how communities are formed, and even how countries interact on a global stage. So, exploring these terms helps us better grasp the complexities of human diversity and the social structures we live within, which is quite interesting, really.
Ethnicity: A Shared Cultural Tapestry
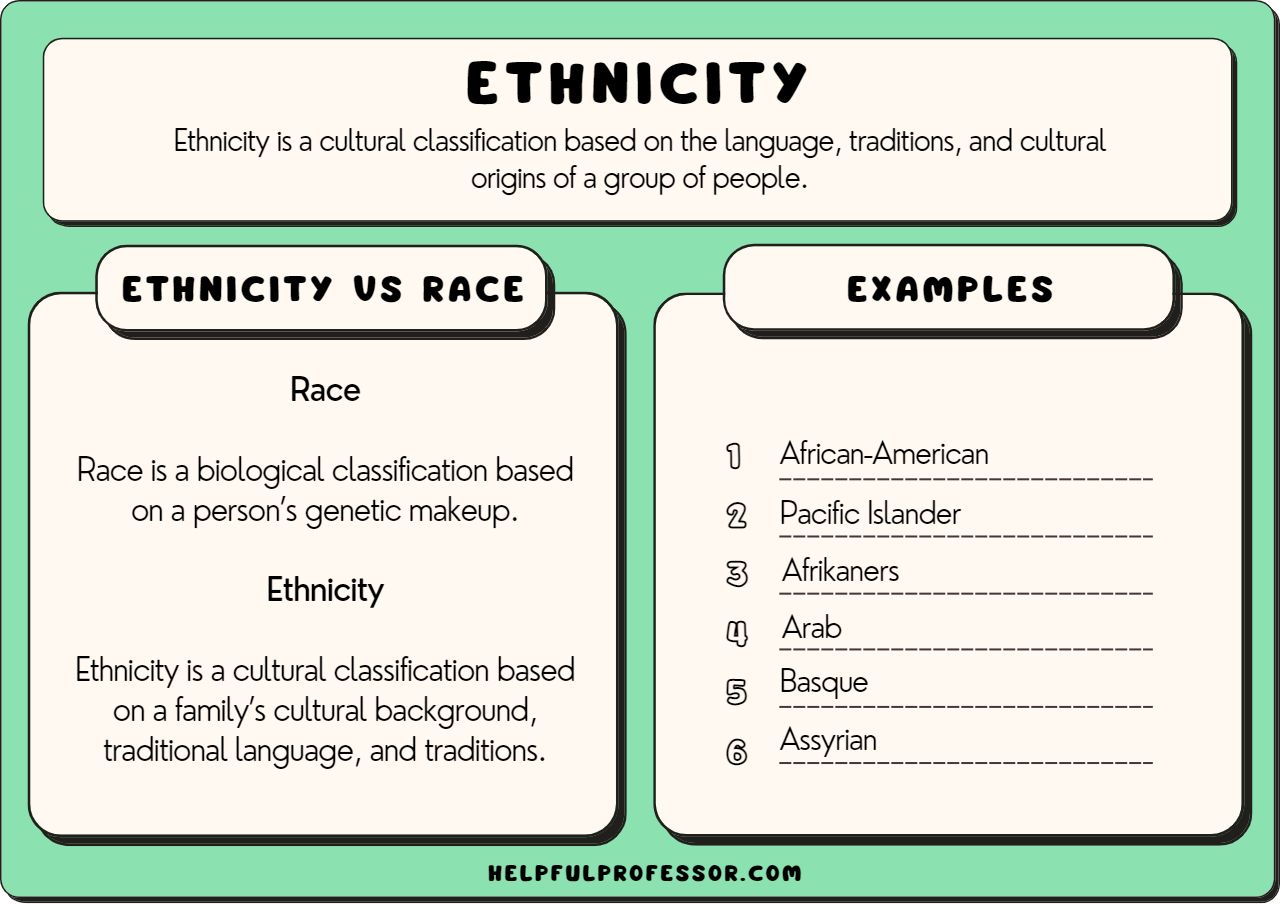
Ethnicity refers to a group of people who identify with each other based on shared attributes, you know, like culture, language, history, society, ancestry, or a common origin. It's a cultural category based on shared practices, and it often highlights the richness and diversity of human societies. This shared background shapes how people see themselves and their place in the world, often existing apart from strict geographical or legal boundaries.
Think of it this way: ethnicity is shaped by cultural factors such as language, traditions, and historical experience. It’s about markers acquired from the group with which one shares cultural, traditional, and familial bonds. For instance, within a single country, numerous ethnicities might coexist, each celebrating its unique traditions, foods, or languages. This shows how ethnicity can be very diverse, even within one nation, as a matter of fact.
There are thousands of ethnic groups in the world, each with its own unique story and way of life. This concept is a social construct, meaning it’s something society has created and agreed upon, rather than a fixed biological fact. It defines a group's identity and can be based on factors such as shared heritage, customs, or even religion, so it's quite broad.
The Cultural Heartbeat of Ethnicity
The cultural heartbeat of ethnicity is really about the shared customs and traditions that bind a group together. This includes everything from the language they speak to the stories they tell, the music they create, and the food they enjoy. It’s a very personal and deeply felt connection, often passed down through generations, you see.
For example, think about a specific holiday or a traditional dish that your family prepares. These are often tied to your ethnic background, reflecting practices that have been part of your group's history for a long time. These shared experiences create a sense of belonging and a collective identity, which is pretty powerful, actually.
Ethnicity helps people understand their roots and where they come from. It provides a framework for cultural expression and community building. This cultural identity, based on shared practices, gives groups a unique flavor and contributes to the overall diversity of human societies, which is quite beautiful, really.
Ethnicity and Race: A Different Story
It’s important to clarify that ethnicity is different from race, though these terms are often tangled up. Race, as my text points out, is a social construct based on physical traits, like skin color, bone structure, or hair texture. It's often understood as a division of human beings depending on their biological attributes, so it's a bit different, you know.
The most fundamental difference between ethnicity and race is that ethnicity is about cultural identity, while race is about physical appearance. Race refers to a person's physical characteristics, whereas ethnicity refers to cultural markers acquired from shared cultural, traditional, and familial bonds. There are only a few major subdivisions of human beings, often called races, but there are thousands of ethnic groups, which is a pretty big distinction.
So, while race is often based on visible characteristics, ethnicity is shaped by cultural factors such as language, traditions, and historical experience. Ethnicity highlights shared cultural heritage, customs, and traditions. The words "race" and "ethnicity" have become so entangled in meaning and use that pulling them apart is a complicated, but necessary, process, to be honest.
Nationality: Your Legal Tie to a Country
Nationality, meanwhile, is more aligned with legal parameters, citizenship, and geopolitical boundaries. It relates to the country one identifies with, either by birth or by naturalization. This is a legal relationship between an individual and a state, which means it comes with specific rights and responsibilities, like voting or carrying a passport, so it's quite different from ethnicity.
It’s a formal status, often determined by birth within a country’s territory, descent from a citizen parent, marriage to a citizen, or through a process called naturalization. This legal bond signifies membership in a specific nation. Unlike ethnicity, which is about shared culture, nationality is about your official connection to a particular country, you know, a place on the map.
There are about 156 countries in the world, and as such, roughly 156 nationalities. While ethnicity often highlights the richness and diversity of human societies, nationality is about the country one has a legal relationship with. It’s a very clear-cut concept, based on laws and borders, which is pretty straightforward, actually.
How Nationality Is Formed
Nationality is primarily formed through legal means, as I was saying. The most common way is by birth within a country's territory, which is called "jus soli" or "right of soil." So, if you're born in a certain country, you typically become a citizen of that country, which is pretty simple, right?
Another common way is through "jus sanguinis" or "right of blood," meaning you acquire nationality through descent from a citizen parent, regardless of where you were born. So, even if you're born abroad, if one of your parents is a citizen of a particular country, you might also be a citizen of that country, you know.
Additionally, nationality can be acquired through marriage to a citizen or through naturalization, which is a process where a non-citizen applies for and is granted citizenship. This process usually involves meeting certain requirements, like living in the country for a specific period, passing a civics test, or pledging allegiance. It’s a formal path to becoming a legal member of a nation, and it can be quite a detailed process, as a matter of fact.
Nationality and Its Global Reach
Nationality has a very practical and global reach, affecting everything from travel to international relations. Your nationality determines which passport you hold, allowing you to travel to certain places without a visa, or requiring you to obtain one for others. It also dictates your rights and protections when you are abroad, which is pretty significant, really.
It’s the legal relationship between an individual and a state, and this relationship is recognized by other countries around the world. For instance, when you apply for a job or enroll in a school in another country, your nationality is often a key piece of information needed. It's a fundamental aspect of how individuals are categorized and recognized on a global scale, you know.
This concept is about membership in a specific nation, often tied to citizenship or country of birth. It’s a very tangible connection to a particular country, with all the legal and political implications that come with it. Nationality, in essence, defines your official belonging to a country, and it's a concept that has shaped geopolitics and individual lives for centuries, so it's quite a powerful idea.
The Intersections and Differences Between the Two
Ethnicity and nationality are two distinct concepts that often intersect but have different meanings, you know. Ethnicity refers to a person's cultural and ancestral background, including shared customs, traditions, language, and heritage. Nationality, meanwhile, is more aligned with legal parameters, citizenship, and geopolitical boundaries. One is about culture, the other about legal status, so they are quite different.
A key difference is that ethnicity is a social construct that defines a group's identity, often based on factors such as race, religion, or shared history. It’s something you're born into culturally, and it’s about a shared way of life. Nationality, on the other hand, is a legal status based on citizenship, determined by birth, descent, marriage, or naturalization. It's about your official tie to a country, which is pretty clear-cut.
For example, a person might be ethnically Chinese but hold American nationality. This means they share cultural heritage, traditions, and perhaps language with people of Chinese ethnicity, but they are legally citizens of the United States. Similarly, someone could be ethnically Kurdish but have Iraqi, Syrian, or Turkish nationality, as the Kurdish people are spread across multiple countries without a state of their own. This illustrates how ethnicity can exist apart from national borders, which is quite interesting, really.
While ethnicity often highlights the richness and diversity of human societies, nationality is about the country one identifies with, either by birth or by naturalization. Ethnicity often cannot be changed, as it's deeply rooted in ancestry and culture, though cultural practices can evolve. Nationality, however, can be changed through legal processes like naturalization, though my text does state it's "not possible to change one," which perhaps refers to the original nationality by birth in some contexts. Anyway, the core distinction remains: one is cultural identity, the other is legal belonging.
Why Understanding These Concepts Is Important
Understanding the differences between ethnicity and nationality is pretty important for a few reasons, you know. First, it helps us appreciate the incredible diversity of human experience. When we recognize that a country can be home to many different ethnic groups, it broadens our perspective and encourages respect for various cultural expressions. It’s like seeing all the different colors in a painting, rather than just one shade, which is quite beautiful.
Second, it helps to avoid misunderstandings and stereotypes. Assuming someone's ethnicity based on their nationality, or vice versa, can lead to incorrect assumptions about their culture, beliefs, or background. Knowing these distinctions helps us communicate more accurately and respectfully with people from all walks of life. It promotes a more inclusive way of thinking, which is really valuable, actually.
Finally, grasping these concepts helps us make sense of global events and social issues. Discussions about identity, migration, and human rights often involve these terms, and a clear understanding allows for more informed conversations. It helps us see how race, ethnicity, and nationality are concepts that have influenced history and society, but also have different meanings and interpretations, so it's pretty essential for navigating the world today.
To learn more about cultural identity on our site, and to explore the complexities of global citizenship, we have other resources available. Understanding these terms helps us better understand what the terms mean and when they might overlap, allowing us to see examples of how ethnicity and nationality relate to a person's identity, culture, and citizenship in various countries and regions, to be honest.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between ethnicity and nationality?
The main difference is that ethnicity refers to a person's cultural and ancestral background, including shared customs, traditions, and language, while nationality denotes membership in a specific nation, often tied to citizenship or country of birth. So, one is about shared culture, the other about legal status, you know.
Can a person have more than one ethnicity or nationality?
A person can certainly identify with more than one ethnicity, especially if they come from a mixed background or have strong ties to different cultural groups. Regarding nationality, some countries allow dual citizenship, meaning a person can legally hold more than one nationality at the same time, which is pretty common in today's world, actually.
Why are ethnicity and race often confused?
Ethnicity and race are often confused because both relate to group identity, but race is traditionally understood as being based on physical characteristics like skin color or facial features, while ethnicity is about cultural identity, shared traditions, and heritage. The words have become so entangled, as a matter of fact, that it takes effort to distinguish them.

Difference between Race and Ethnicity - Race vs. Ethnicity - GeeksforGeeks
50 Examples of Ethnicities (A to Z List) (2025)

Race vs. Ethnicity: A guide - Bridging the Gap to Leadership